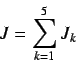Next: GETAWAY[4,5,6]
Up: Molecular Descriptors
Previous: BCUT (aka Burden Eigenvalues)[2,3,14]
Contents
These indices describe charge transfer between pairs of atoms and
therefore global charge transfer in a molecule. To obtain
definitions of the indices we first define the matrix
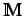 as
as
where 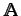 is the adjacency matrix and
is the adjacency matrix and
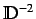 is
the reciprocal square distance matrix. Note that the diagonal
elements of the distance matrix remain the same.
is
the reciprocal square distance matrix. Note that the diagonal
elements of the distance matrix remain the same. 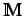 is
the Galvez matrix and is a square unsymmetric
is
the Galvez matrix and is a square unsymmetric 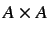 matrix where
matrix where 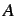 is the number of atoms in the molecule.
is the number of atoms in the molecule.
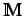 gives rise to an unsymmetric charge term
matrix,
gives rise to an unsymmetric charge term
matrix,
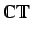 defined as
defined as
where 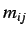 are elements of
are elements of 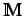 and
and 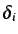 is the
vertex degree of atom
is the
vertex degree of atom 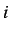 .
.
The diagonal entries of
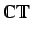 represent the topological
valence of the atoms and the off diagonal entries
represent the topological
valence of the atoms and the off diagonal entries 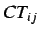 represent
the amount of charge transferred from atom
represent
the amount of charge transferred from atom 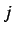 to atom
to atom 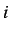 . If
heteroatoms are to be considered the diagonal entries of
. If
heteroatoms are to be considered the diagonal entries of
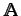 can be substituted by Paulings atom
electronegativity or valence vertex degree (for an atom
can be substituted by Paulings atom
electronegativity or valence vertex degree (for an atom 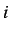 is given
by
is given
by
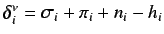 where
where
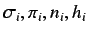 are the number of sigma, pi, lone pair electrons and hydrogen
atoms respectively).
are the number of sigma, pi, lone pair electrons and hydrogen
atoms respectively).
For each path length 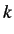 we can define a topological charge
index,
we can define a topological charge
index, 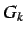 as
as
where
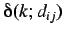 is the Kronecker delta,
is the Kronecker delta,
where 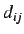 are elements of the distance matrix. Thus
are elements of the distance matrix. Thus 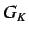 represents the total charge transfer between atoms at a topological
distance
represents the total charge transfer between atoms at a topological
distance 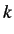 . The maximum number of
. The maximum number of 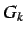 terms equals the
topological diameter,
terms equals the
topological diameter, 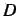 .
.
The average topological charge index, 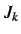 is defined as
is defined as
and the global topological charge index, 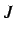 , is defined as
, is defined as
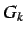 values (and hence
values (and hence 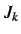 &
& 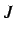 values) are set to zero for
values) are set to zero for 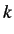 values greater than
values greater than 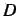 .
.




Next: GETAWAY[4,5,6]
Up: Molecular Descriptors
Previous: BCUT (aka Burden Eigenvalues)[2,3,14]
Contents
2003-06-16
![]() gives rise to an unsymmetric charge term
matrix,
gives rise to an unsymmetric charge term
matrix,
![]() defined as
defined as
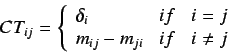
![]() represent the topological
valence of the atoms and the off diagonal entries
represent the topological
valence of the atoms and the off diagonal entries ![]() represent
the amount of charge transferred from atom
represent
the amount of charge transferred from atom ![]() to atom
to atom ![]() . If
heteroatoms are to be considered the diagonal entries of
. If
heteroatoms are to be considered the diagonal entries of
![]() can be substituted by Paulings atom
electronegativity or valence vertex degree (for an atom
can be substituted by Paulings atom
electronegativity or valence vertex degree (for an atom ![]() is given
by
is given
by
![]() where
where
![]() are the number of sigma, pi, lone pair electrons and hydrogen
atoms respectively).
are the number of sigma, pi, lone pair electrons and hydrogen
atoms respectively).
![]() we can define a topological charge
index,
we can define a topological charge
index, ![]() as
as
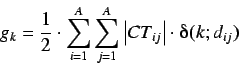
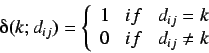
![]() is defined as
is defined as