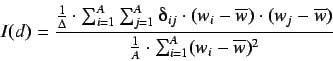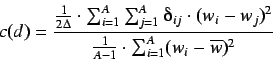Next: BCUT (aka Burden Eigenvalues)[2,3,14]
Up: Molecular Descriptors
Previous: Contents
Contents
Subsections
These are based on an autocorrelation function, 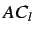 defined as
defined as
where 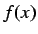 is a function and
is a function and 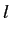 is the lag representing an
interval of
is the lag representing an
interval of 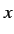 .
. 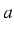 and
and 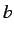 define the total studied interval of
the function.
define the total studied interval of
the function. 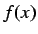 is usually a time dependent function.
is usually a time dependent function.
For an ordered sequence of 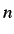 values
values 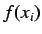 we can calculate
we can calculate
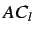 by
by
where 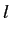 is the lag and assumes the values from 1 to
is the lag and assumes the values from 1 to 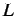 where
where
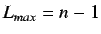 .
. 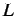 is usually less than 8.
is usually less than 8.
A property of the autocorrelation value is that it does not change
when the origin of the 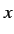 variable is changed.
variable is changed.
To get spatial autocorrelation descriptors 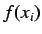 is a physico
chemical property calculated for all atoms such as atomic mass,
polarizability etc. Thus atoms represent the discrete points
is a physico
chemical property calculated for all atoms such as atomic mass,
polarizability etc. Thus atoms represent the discrete points 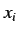 and the atomic properties for each atom represent the function value
at that point. In this case the lag
and the atomic properties for each atom represent the function value
at that point. In this case the lag 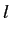 is defined as the
topological distance
is defined as the
topological distance 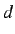 (ie topological distance
(ie topological distance 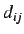 between
two graph vertices
between
two graph vertices 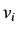 and
and 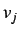 is the number of edges in the
shortest path between these two vertices).
is the number of edges in the
shortest path between these two vertices).
Moreau Broto
Autocorrelation
Also known as Autocorrelation of a Topological Structure (ATS). The
ATS descriptor describes how a property is distributed along the
topological structure.
It is
a spatial autocorrelation on a molecular graph defined as
where 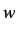 is any atomic property,
is any atomic property, 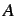 is the atom number (total
number of atoms),
is the atom number (total
number of atoms), 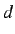 is the considered topological distance,
is the considered topological distance,
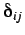 is the Kronecker delta,
is the Kronecker delta,
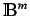 is the
is the 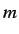 'th
order binary sparse matrix (a matrix whose elements are equal to 1
only for vertices
'th
order binary sparse matrix (a matrix whose elements are equal to 1
only for vertices 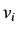 and
and 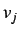 at a distance
at a distance 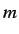 )and
)and
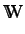 is the
is the 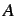 dimensional
vector of atomic properties.
dimensional
vector of atomic properties.
For each property 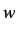 the set of autocorrelation terms defined for
all existing distances in the graph is the ATS descriptor
defined as
the set of autocorrelation terms defined for
all existing distances in the graph is the ATS descriptor
defined as
where 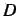 is the topological diameter (maximum distance in the
graph).
is the topological diameter (maximum distance in the
graph).
The average spatial autocorrelation descriptors exclude any
dependence on the molecular size and are obtained by dividing each
term by the corresponding number of contributions, ie,
where 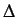 is the sum of the Kronecker deltas, ie the number of
the vertex pairs at a distance
is the sum of the Kronecker deltas, ie the number of
the vertex pairs at a distance 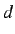 .
.
ATS descriptors for 3D geometries are based on the geometry matrix
(whose entries 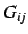 are the Euclidean distance between atoms
are the Euclidean distance between atoms 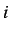 and
and 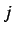 )
)
This is an index of spatial correlation defined by
where 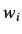 is an atomic property and
is an atomic property and 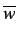 is the average
value over the whole molecule,
is the average
value over the whole molecule, 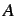 is the atom number,
is the atom number, 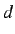 is the
topological distance,
is the
topological distance, 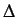 is the sum of the Kronecker deltas, ie the number of
the vertex pairs at a distance
is the sum of the Kronecker deltas, ie the number of
the vertex pairs at a distance 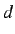 .
Defined as
.
Defined as
where the symbols are same as in the Moran coefficient. This is a
distance type function and its range is ![$[0,\infty]$](img36.png)




Next: BCUT (aka Burden Eigenvalues)[2,3,14]
Up: Molecular Descriptors
Previous: Contents
Contents
2003-06-16
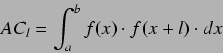
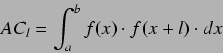
![]() values
values ![]() we can calculate
we can calculate
![]() by
by
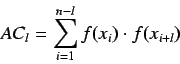
![]() variable is changed.
variable is changed.
![]() is a physico
chemical property calculated for all atoms such as atomic mass,
polarizability etc. Thus atoms represent the discrete points
is a physico
chemical property calculated for all atoms such as atomic mass,
polarizability etc. Thus atoms represent the discrete points ![]() and the atomic properties for each atom represent the function value
at that point. In this case the lag
and the atomic properties for each atom represent the function value
at that point. In this case the lag ![]() is defined as the
topological distance
is defined as the
topological distance ![]() (ie topological distance
(ie topological distance ![]() between
two graph vertices
between
two graph vertices ![]() and
and ![]() is the number of edges in the
shortest path between these two vertices).
is the number of edges in the
shortest path between these two vertices).
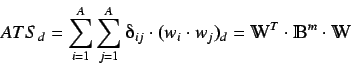
![]() the set of autocorrelation terms defined for
all existing distances in the graph is the ATS descriptor
defined as
the set of autocorrelation terms defined for
all existing distances in the graph is the ATS descriptor
defined as
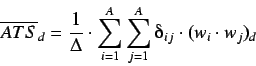
![]() are the Euclidean distance between atoms
are the Euclidean distance between atoms ![]() and
and ![]() )
)