


Next: Radial Basis Function Networks
Up: Neural Networks
Previous: Back Propagation
Subsections
- Approximation of the input space: The feature map
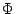 represented by a set of synaptic weight vectors
represented by a set of synaptic weight vectors
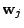 in the output space
in the output space
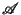 provides a good approximation
to the input space
provides a good approximation
to the input space
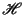
- Topological ordering: The feature map
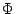 computed by
the SOM algorithm is topologically ordered in the sense that the
spatial location of a neuron in the lattice corresponds to a
particular domain or feature of input neurons.
computed by
the SOM algorithm is topologically ordered in the sense that the
spatial location of a neuron in the lattice corresponds to a
particular domain or feature of input neurons.
- Density matching: The feature map
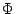 reflects
variations in the statistics of the input distribution: regionms
in the input space
reflects
variations in the statistics of the input distribution: regionms
in the input space
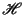 from which sample vectors
from which sample vectors
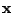 are drawn with a high probability of occurance are
mapped onto larger domains of the output space
are drawn with a high probability of occurance are
mapped onto larger domains of the output space
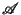 and
therefore with better resolution than regions in
and
therefore with better resolution than regions in
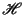 from which sample vectors are drawn with a low probability of
occurance.
from which sample vectors are drawn with a low probability of
occurance.
- Feature selection: Given data from an input space with a
non linear distribution the SOM is able to select a set of best
features for approximating the underlying distribution



Next: Radial Basis Function Networks
Up: Neural Networks
Previous: Back Propagation
2003-06-08